Musicians and video directors: discover how thousands of prompts, frame-by-frame tweaks, and human direction turn AI-generated music videos into handcrafted visual stories.
Critics dismiss AI music videos as lazy shortcuts that threaten real creativity. They point to sloppy outputs and claim the technology replaces human artistry with button-mashing automation. But this view misses the reality of how professional AI music videos get made.
The truth is more complex. While 92% of creators use AI already, the best AI music videos require intensive human direction, iterative refinement, and artistic vision. They’re not replacing traditional filmmaking but fostering innovation by expanding what’s possible for musicians with limited budgets. If you’re wondering which platform suits your creative vision, I’ve tested and compared the best AI music video generators to help you make an informed choice.
Here are 7 behind-the-scenes secrets that reveal why AI music videos represent genuine artistry, not lazy work, answering the question: is AI art really art?
JUMP LINKS:
Professional AI music videos demand the same creative planning as traditional shoots. The difference lies in execution method, not artistic rigor. Whether you’re a solo artist or working with a director, these insights show why quality AI videos require serious craft.
1. Thousands Of Prompts Create One Coherent Scene
AI music videos start with extensive prompt engineering, not single commands. Directors write dozens of micro-prompts per scene to control lighting, camera angles, character positioning, and visual style, demonstrating the intricacies of ai music video editing.
Professional filmmaker Max Joseph spent 250 hours creating an AI music video for Arctic Monkeys‘ “A Certain Romance” using Google Veo. His process involved iterating hundreds of prompts to maintain narrative coherence across the 4-minute video.
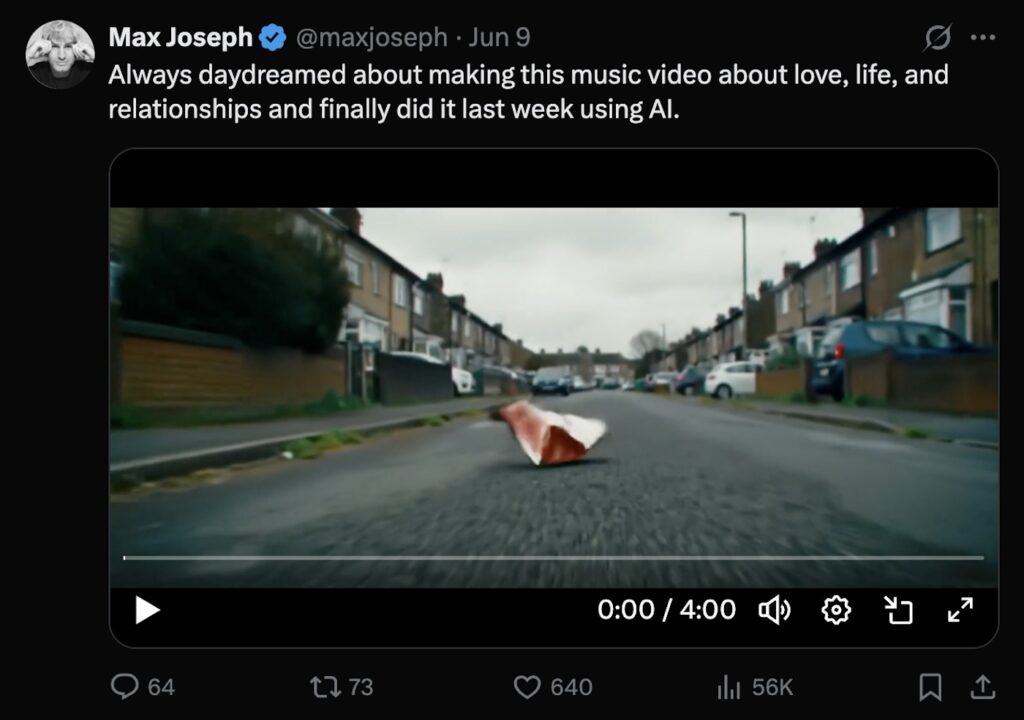 Credit: Max Joseph X Post
Credit: Max Joseph X Post
Key prompt strategies that ensure consistency:
- Save successful prompt seeds and parameters for reuse
- Write detailed scene descriptions before generating footage
- Test character positioning prompts across multiple angles
- Document lighting and color palette instructions per sequence
- Create prompt templates for recurring visual elements
Example: Washed Out’s “The Hardest Part” director Paul Trillo stitched dozens of Sora-generated zoom sequences, guiding style per decade and rotoscoping transitions. The 4:02 runtime represents the longest Sora production to date, requiring frame-level planning for narrative coherence.
Pro tip: Treat each prompt like a storyboard panel. Write specific instructions for camera movement, subject placement, and visual mood rather than generic descriptions.
2. Frame-By-Frame Editing Takes Weeks, Not Minutes
Quality AI music videos require extensive post-production work. Directors spend 30% of their timeline on manual rotoscope cleanup, color grading, and rhythm synchronization after AI generation.
Don Diablo’s “BLACKOUT” video combined RTX-powered local generation with cloud animation via Kling AI. Despite using cutting-edge tools, the project probably took weeks to complete with significant human editing between AI passes.
The reality of AI video post-production:
- Manual cleanup of visual artifacts in every frame
- Color correction to match lighting across generated sequences
- Audio synchronization requires precise timing adjustments
- Character consistency fixes through rotoscoping techniques
- Transition smoothing between AI-generated clips
Phoenix’s “Alpha Zulu” video used Stable Diffusion to animate Louvre masterpieces lip-syncing, with manual cleanup per frame. The video hit 10 million views and earned Rolling Stone praise for its “AI-cubist aesthetic.”
Quick rule: Allocate at least 30% of your production timeline to human editing passes. AI generates raw material, but human refinement creates the final product.
3. Lip Sync Perfection Demands Technical Mastery
Achieving convincing lip sync in AI videos requires sophisticated technology and meticulous attention to detail. Tools like HeyGen’s AI lip sync generator use deep neural networks, computer vision, and speech recognition to match mouth movements with audio tracks.
The process involves multiple technical challenges:
Key technical requirements for quality lip sync:
- High-resolution source footage with clear facial features
- Professional audio recording with minimal background noise
- Frame-by-frame analysis of phoneme-to-viseme mapping
- Manual adjustment of timing and mouth shape accuracy
Quick rule: Good lighting and video resolution make the difference between amateur and professional results. Poor source material creates artifacts that break the illusion.
Professional productions allocate significant time to lip sync refinement. The AI provides the foundation, but human editors fine-tune timing, adjust sensitivity settings, and correct synchronization errors frame by frame.
Phoenix’s “Alpha Zulu” video used Stable Diffusion to animate Louvre masterpieces lip-syncing to the track, with manual cleanup performed on every single frame to achieve the final result.

4. Storytelling Requires Deep Creative Planning
 Arctic Monkeys – A Certain Romance (AI Music Video by Max Joseph)
Arctic Monkeys – A Certain Romance (AI Music Video by Max Joseph)
Max Joseph is a professional filmmaker. His 250-hour Arctic Monkeys project most definitely began with extensive storyboarding and narrative development. Professional AI music video creators develop detailed scripts and mood boards before generating any footage.
The storytelling process mirrors traditional filmmaking:
Essential pre-production steps for AI music videos:
- Script development with scene-by-scene breakdowns
- Mood board creation for visual consistency
- Character development and visual style guides
- Shot list planning with specific prompt strategies
Example: Washed Out’s “The Hardest Part” director Paul Trillo stitched dozens of Sora-generated zoom sequences, guiding style per decade and rotoscoping transitions for narrative coherence.
Pro tip: Your story concept must be crystal clear before you start generating footage. Vague ideas produce inconsistent results that require extensive post-production fixes.
The most successful AI music videos start with compelling narratives. Creators spend weeks developing concepts that work within AI generation constraints while serving the song’s emotional arc.
Linkin Park’s “Lost” video hit 16 million YouTube views in 8 days because Web3 studio Shibuya crafted a meticulous prompt-plus-editorial process that supported the song’s themes.

5. Custom Model Training Ensures Visual Consistency
Professional AI music videos use custom-trained models rather than generic generators. Directors train LoRA or Dreambooth models on band imagery to maintain character likeness across frames.
Don Diablo trained custom face models using Stable Diffusion in ComfyUI for character consistency throughout “BLACKOUT.” This approach prevents the jarring character shifts that plague amateur AI videos.
Training requirements for consistent results:
- Collect 50-100 high-quality reference images per character
- Use consistent lighting and angles in training dat
- Test model outputs across different poses and expressions
- Fine-tune parameters to avoid overfitting
- Document successful training settings for future projects
YACHT’s “(Downtown) Dancing” lyric video used experimental AI typeface generation for each lyric, with hand-keyframed motion graphics. Proving early AI integration still required human typography and timing expertise. The video was created by the designer and visual artist Barney McCann.
Example: Grimes leveraged AI for her Coachella 2024 performance. The performance was notably marred by technical issues. She later apologized, citing problems like outsourcing track preparation and BPM settings—factors that disrupted the show
The visual production for her set was handled by XiteLabs, who deployed an advanced XR/AR pipeline. They created immersive visuals—like a “Grimes fairy” that physically broke free from her DJ booth—with real-time motion capture (via MOVE AI), Unreal Engine, Resolume media servers, and live VJ operations
Top-tier AI music videos use multiple specialized tools rather than single platforms. Directors combine local GPU processing for rapid iteration with cloud-based models for high-fidelity final renders.
The strategic tool combination approach:
- Local Stable Diffusion for rapid still-frame exploration
- Cloud video models like Sora, Kling, and Runway for motion
- Traditional editing software for final assembly and effects
- Custom scripts to batch process generated content
- Hardware optimization for faster iteration cycles
Don Diablo’s hybrid pipeline rendered stills on RTX 5090 hardware before uploading to Kling AI for motion generation. This approach balanced speed with quality while managing cloud computing costs.
Pro tip: Build your workflow around iteration speed first, final quality second. Rapid testing prevents expensive mistakes in cloud rendering.
The global AI video generator market reached $554.9 million in 2023 and forecasts $1.96 billion by 2030, indicating professional adoption beyond hobbyist experimentation.
7. Human Oversight Prevents Quality Disasters
In a report by Adobe and Econsultancy 57% of creative professionals cite “ensuring quality and trust” as their biggest AI challenge. Professional AI music videos require constant human judgment to catch artifacts, maintain narrative flow, and ensure brand consistency.
Quality control checkpoints that separate professional work:
- Review every generated frame for visual artifacts
- Test character consistency across scene transitions
- Verify lip-sync accuracy in performance sequences
- Check brand guidelines compliance throughout
- Validate technical specifications for distribution platforms
The Washed Out “The Hardest Part” video faced fan criticism for “AI gimmick” aesthetics, sparking Rolling Stone debate about AI art authenticity. This backlash highlights why quality control matters for artist reputation.
Example: Fake America’s Got Talent AI music videos hit 44 million YouTube views by exploiting poor quality control, demonstrating how sloppy AI work damages the medium’s credibility.
 Credit: YouTube Az Ai
Credit: YouTube Az Ai
Quick rule: Every AI-generated element in the video creation process needs human approval before final assembly by a music video editor. Automation handles generation, but humans handle curation.
Commercial Success Proves Audience Acceptance of AI music videos
Linkin Park’s AI-animated “Lost” hit 16 million YouTube views in 8 days and topped Billboard’s Rock & Alt Airplay Chart. To create the video the AI music video generator Kaiber was used. The video crossed 100 million views by mid-2025, becoming the band’s fastest-growing post-2010 release.
The Linkin Park video for ‘Lost’ shows a more obvious use of AI, but the comments section tells a different story – no one is complaining about the technology. The band created the video as a tribute to Chester Bennington’s memory, and fans seem to appreciate that respect.
This isn’t Linkin Park’s first time using anime-style visuals either. Their 2003 video for ‘Breaking the Habit’ featured rotoscoping animation directed by DJ Joe Hahn and created by Studio Gonzo in Japan. When AI is used thoughtfully and fits the band’s established style, audiences focus on the emotion and artistry rather than the tools behind it.
Commercial performance metrics that validate AI music videos:
- “Lost” became first rock song in 10 years to debut at #1 on Billboard Rock & Alt Airplay
- Washed Out’s Sora-generated video garnered 1 million views in its first week
- Phoenix’s AI-animated “Alpha Zulu” reached 10 million views with critical acclaim
- Don Diablo’s “BLACKOUT” premiered at Tomorrowland to positive audience response
These results prove audiences judge videos by entertainment value, not production method. Quality execution matters more than the tools used to create it.
Workers using generative AI daily boost productivity 33% per hour of use, supporting the business case for AI integration when applied thoughtfully.
Example: In the comments under Phoenix’s Alpha Zulu video, I found several people who genuinely loved what they saw. They weren’t questioning how it was made or complaining about the process – they were just saying they enjoyed the video.
Bonus tip: Legal Complexity Requires Careful Documentation
 Imagecredit: Wikimedia Commons (AgnosticPreachersKid)
Imagecredit: Wikimedia Commons (AgnosticPreachersKid)
AI music videos face copyright ambiguity that demands meticulous documentation. U.S. courts deny full copyright protection to works generated “start-to-finish” by AI without human authorship, making process documentation crucial for legal protection.
Essential documentation for copyright protection:
- Record all human creative decisions and interventions
- Document prompt writing and iteration processes
- Save evidence of manual editing and post-production work
- Credit AI model weights and training datasets used
- Register works under mixed-media copyright categories
Cloud video models bill per second of generation, with Runway Gen-3 charging 10 credits per second up to 20 seconds. Cost management requires careful planning and documentation of usage.
 Screenshot
Screenshot
Pro tip: Publish behind-the-scenes process reels showing human involvement. This documentation supports copyright claims while building audience appreciation for the craft involved.
Example: The generative AI market projects $109.4 billion by 2030 with 37.6% annual growth, indicating long-term industry investment in professional AI tools rather than amateur shortcuts.
Quick recap of the key takeaways:
- Thousands of iterative prompts create coherent scenes, not single commands
- Frame-by-frame editing requires weeks of human refinement work
- Technical mastery of lip sync technology demands specialized expertise
- Storytelling and pre-production planning mirror traditional filmmaking processes
- Custom model training ensures character consistency across sequences
- Hybrid workflows strategically combine multiple specialized AI tools
- Human quality control prevents artifacts and maintains brand standards
- Commercial success proves audiences value execution over production method
- Legal documentation protects copyright through evidence of human authorship
Which approach will you test first for your next music video project?
AI music videos aren’t one-click hacks. They’re built from thousands of prompts, custom-trained models, and hybrid tools—and about 30% of the timeline goes to cleanup, color, and timing. Humans review every shot and document choices to protect rights.
Most audiences judge results—charting hits, million-view releases—not the method. Bottom line: AI is the toolkit; the art comes from the director’s judgment and persistence.